In today’s hyper-competitive digital landscape, a well-structured semantic SEO content strategy is the backbone of topical authority, brand authority, and lead generation. With over 15 years of experience in SEO, content marketing, and search engine algorithms, we have witnessed firsthand how Google’s ranking factors have evolved from keyword stuffing in the early 2000s to today’s semantic search, topical authority, and user intent-driven optimisation.
Modern SEO content isn’t just about stuffing keywords into articles – it’s about strategic topic clustering, entity based SEO, NLP (Natural Language Processing), structured data and E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority and Trustworthiness) guidelines. The latest Google Helpful Content Update has further cemented the need for human first, high value and engaging content that satisfies search intent and is optimised for algorithmic discoverability.
We offer Semantic SEO driven blog optimisation, long term content planning and scalable content frameworks that achieve sustained organic visibility and conversion driven content performance. Whether you are a business owner, digital marketer or SEO strategist this framework will empower you to rank higher, attract qualified traffic and build brand authority through content excellence.
Our Semantic SEO Service Details
We implement a semantic content network in your website to achieve topical authority by covering diverse topical intents within a set of content using different clusters. Executing a semantic SEO strategy gets a website to a search engine’s trusted websites list. By doing entity-based SEO, your website’s pages will rank faster and higher. Also, semantic content network implementation protects a website from sudden rank drop due to search engine core algorithm updates.
Semantic SEO Service We Offer
- Semantic SEO strategy to build topical authority
- Entity-based optimisation using topic clusters & internal linking
- Topical map creation to structure content for long-term SEO
- Content creation using NLP (Natural Language Processing)
- Schema markup implementation (e.g. Thing, FAQ, Article)
- EEAT-focused optimisation (Expertise, Experience, Authority, Trust)
- Google Knowledge Graph integration
- Author SEO & brand trust-building
- Content audit, structured internal linking, and review of site-wide entity flow
Deliverables
- Custom-built Topical Map
- In-depth, NLP-formatted content
- Interlinked content clusters (pillar & supporting pages)
- Schema (structured data) for Knowledge Graph compatibility
- EEAT signals through expert-driven content & author profiles
- Entity-rich SEO audit and content plan
- Monthly reporting & performance tracking
- Ongoing improvements to semantic structure over time
- Results usually appear from 4 to 7 months of continuous work.
Pricing
- Initial Topical Map costs £500
- Monthly SEO package costs between £1500 and £4,000
- Customers can set their budget and customise the service depending on the budget.
- The overall cost may vary depending on your website’s recent performance. Fixing website errors or preparing the website for semantic SEO is outside this price range.
Semantic SEO Success
Here is an example that shows how entity-based SEO strategy boost a website rank just after a few core algorithm update. Below picture represents a significant impression and click increase of one of our UK-based accountancy client’s websites.

We took only three months to make our client’s website as an authoritative trusted website. In three months time, Google Smart Brain algorithm started to trust the website by deep understanding the knowledge graph that we have created through entity-based semantic content distribution.
In total, we published 51 in-depth content according to our topical map. We were lucky that our UK-based client didn’t have any budget constraints. Monthly spending helped us to accelerate the process and bring results faster.
Here’s what we did with semantic SEO:
- Keyword research and search intent research to find a strategy that actually outranks the competitors.
- Creation of topical map targeting faster topical authority.
- Designing entity-based content brief according to topical map.
- Writing articles in NLP format, targeting rich answer snippets and maximum search intent coverage.
- Targeting large number of quiries under a parent topic and optimise the content for all of the queries.
- Targetting PAA questions and optimise website for Answer Search Optimisation.
- Implementation of an authoritative content network following a roadmap.
- Performing author SEO for EEAT signals.
- Performing link-building as a supporting optimisation.
Below we illustrated different sections of topical authority and semantic optimisation for your understanding.
Request a Quote
Price of semantic SEO varies depending on the type of your business, competitors you are competing and the number of topic clusters you are needing. If you are damn serious about watching your website like the proof we have just shared – request a quote with details. We will get back.
What is Semantic SEO & Why is it the Future of Search Rankings?
Semantic SEO is an advanced search engine optimisation strategy that focuses on optimising for meaning, context and intent not just keywords. It aligns with Google’s evolving algorithms, Natural Language Processing (NLP) and entity-based search indexing to get your content seen and ranked.
Unlike traditional SEO which relied on exact match keywords, Semantic SEO uses related concepts, contextual relationships, and topic clustering to provide a better user experience and improve organic rankings.
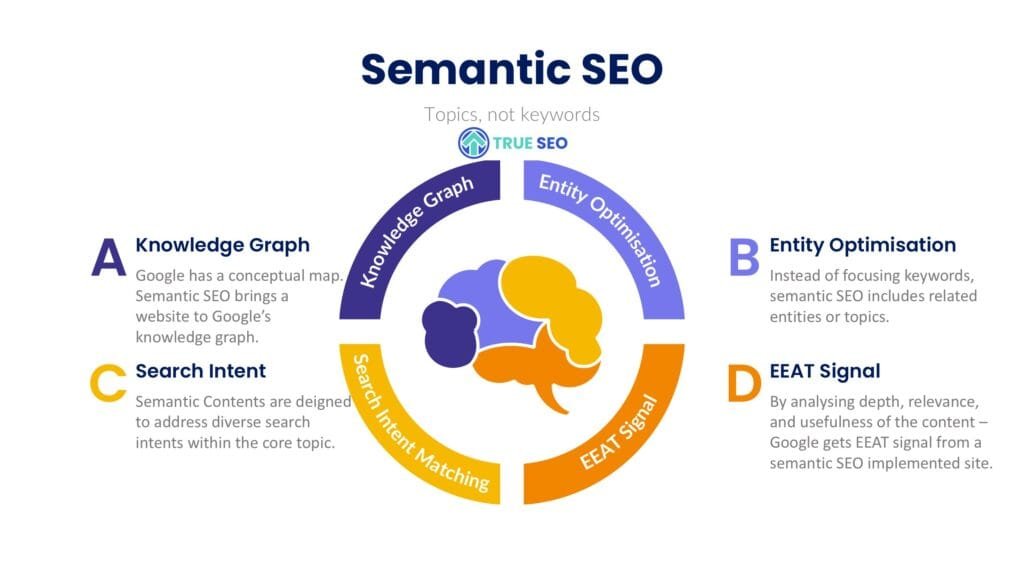
Key Elements of Semantic SEO:
- Entity Based Optimisation → Instead of focussing on keywords, Google now understands entities (people, places, brands, concepts, topics and things) and how they relate.
- Topical Authority & Content Clusters → Google rewards comprehensive coverage of a topic using pillar content and interlinked clusters to establish expertise.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) & Contextual Search → Search engines now interpret the intent behind the query thanks to Google’s BERT & RankBrain algorithms.
- Knowledge Graph & Schema Markup → Google associates entities in a structured way using Knowledge Graph connections and schema markup to understand relationships.
- Search Intent Optimisation → Create content that matches user intent—informational, navigational, transactional or commercial—and improves ranking stability and engagement.
How Semantic Knowledge Grapgh Affects Website Rank?
By a proper semantic content network, a website establishes a clear relation of the entities within the content. The entity based contents appears as a knowledge graph to search engine. Search engine ranks a website with better in-depth knowledge graph. Knowledge graph a tool to assess content depth and topical coverage of any website.
As search engines evolve, google no longer ranks content based on keyword matching. It uses Natural Language Processing (NLP), Google Knowledge Graph and Entity Relationships to understand the meaning, intent and context of a search query. This shift towards Semantic Search allows Google to provide more relevant, authoritative and intent driven search results.
For example, if you search for ‘Apple’, Google will automatically understand that you are looking for a tech brand. google will automatically show the nearest apple store, recent apple device price, any used apple device ads separately and on the right side of your browser – there will other relevant information regards to the apple store and gadgets.
It means, search engine now understands your perspective rather than focusing on keywords. Google Knows who is Steve jobs, How does California is related to Apple, and what is 16 Pro Max!
In simple terms, Google smart brain correlates different topics (entities) with each other from one of its ‘knowledge graph’.
Google constantly updates its knowledge graph to strengthen its SMART Brain knowledge so that visitors get the best result within the soonest.
By updating Google’s knowledge graph, it is easier to understand, predict and solve peoples search perspective.
How Google Uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to Understand Content?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of artificial intelligence (AI) that enables Google to understand and process human language more accurately. Google’s NLP advancements, including BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), MUM (Multitask Unified Model) and RankBrain have changed the way content is indexed and ranked.
How Google Uses NLP to rank a content?
Google uses BERT, RANKBRAIN and MUM to form a systematic Natural Language Processing (NLP) process to understand content and peoples perspective. These algorithm helps google enriching its knowledge graph and detecting the valuable contents on the internet.
A. BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers)
BERT helps Google understand the context of words within sentences, making search results more accurate. BERT analyzes search queries bi-directionally, meaning it looks at words before and after a given term to determine its meaning.
Impact on SEO:
- Optimizing for BERT means writing content that is natural, clear and aligned with user intent.* Keyword stuffing is useless as Google now prioritizes contextual relevance over exact-match keywords.
- Example: A search for “how to catch a bass without a fishing rod” previously might have ranked pages about fishing rods, but now, BERT ensures results focus on alternative fishing techniques.
B. RankBrain (AI-Powered Search Ranking)
Rankbrain understands how valuable a webpage is. If a user clicks a website and leave to another website, Google understand that the webpage was not valuable. But, if a person goes to a website finds his answer, performs an action and do not search for similar answer from other website, Google considers the content as valuable. The main purpose was to use machine learning to refine search results based on user behavior and engagement.
Impact on SEO:
- Websites must focus on user engagement signals (dwell time, CTR, bounce rate) to rank higher.
- Good content and satisfying search intent are essential for strong RankBrain signals.
C. MUM (Multitask Unified Model)
Through MUM, Google understand entire web page including the text, image, videos and other elements such as banners, call to action button and the overall intention of the website. MUM is the Google’s most advanced AI model that understands text, images, video and audio simultaneously.
MUM processes and connects multiple types of content** to improve search relevance. It can also understand complex queries across languages and formats.
Impact on SEO:
- Content must be multimodal—including text, images, videos and structured data for better rankings.
- Example: If a user searches for “hiking in Japan,” MUM can pull relevant blog posts, YouTube videos and infographics in one SERP result.
Google’s Smart Brain is trained enough to know how authentic and deep your content is.
We ensure clients’ content is rich enough to pass EEAT

How Google’s Knowledge Graph Helps Rank Content?
Google’s Knowledge Graph is a massive database of entities – people, places, concepts and things – and their relationships. It helps Google understand context so search results are more accurate and relevant.
Knowledge graph affects search ranking by recognising entities instead of keywords, understands relationship between topics, and uses structured data (schema markup) to improve visibility.
For example, if you search “Leonardo da Vinci”, Instead of just listing web pages, Google shows:
- Semantic connections like his inventions and scientific contributions
- A knowledge panel with his bio
- Related entities like Mona Lisa, Renaissance Art and Michelangelo
Why Semantic Knowledge Graph Matters for SEO?
Knowledge graph defines content context by analyzing entities instead of just keywords, increases visibility for websites connected to recognized Knowledge Graph entities, and improves search engine understanding through structured data and schema markup.
These are the main reasons we prioritize semantic SEO applications while doing on-site SEO for our clients.

How Semantic Entity Relationships Impact Rankings in SEO?
Websites having naturally connected entities throughout the semantic content structure are likely to be crawled more frequent because search engine finds a website useful if there are well-connected topic-related entities within the website content.
Entities are the foundation of semantic search. Google ranks content based on entity relationships, not keyword density. It means,that to get search engines’ attention, your website needs to connect entities (topics) systematically without losing the context of the article and the flow of the information.
A typical SEO expert may gather all or most of the topics into the content but, creating the flow would require technical ability to systematically distribute the weightage of the entities (topics).
For example, A single web page may use 100 entities but there should be only one primary topic (main entity) and the rests would match with the primary entiy’s context. Giving extra emphasis on secondary topics (additional entities) would confuse google while assessing the perspective of the search and the context of your content.
In easy sentences:
How Google Uses Entity Relationships in Website Rankings?
After analysing the entity relationships of a website’s contents, Google starts identifying the name, type, purpose, and connections of the entities. These entity connections help Google to determine the relevance, trustworthiness, authenticity, usefulness, location, and other relevant factors about the website. These analyses and identification help search engines to compare a website with others.
Google also stores the initial ranking data of any website and sets a quality threshold for that website. This is the main reason websites with higher impressions (semantically optimised content) are more likely to rank future posts quickly than others.
However, publishing any less valuable content in the future may reduce a website’s quality threshold and will affect subsequent future rankings of existing and upcoming posts.

Below we break the ranking impacts caused by the entity relationship of a website.
- Google Maps & Local SEO: Location-based entities impact rankings.
- Example: Search for “best Italian restaurants near me” and Google prioritizes businesses connected to “Italian cuisine” in that area.
- E-E-A-T & Topical Authority: Trust signals affect rankings.
- Example: Google prioritizes medical advice from authoritative sources like Mayo Clinic over unknown blogs because of recognized expertise.
- Topical Clusters & Internal Linking: Strengthen entity relevance by grouping related topics together.
- Example: A health website interlinking articles on “Heart Disease”, “Cholesterol Management” and “Healthy Diets” builds stronger topical authority.
By optimizing content around entity relationships, structured data and topic clusters you can improve search relevance, authority and organic rankings.
How Topical Authority Wins in Modern SEO?
Topical authority works through a well-designed topical map, content clustering, semantic relevance & internal linking, and in-depth content. It is a combination. Applying one item or inaccurate application may lead to a rank drop. Focusing on topical coverage rather than isolated keywords is the key to long-term SEO success.
- Content Clustering: Building topic clusters around a core topic tells Google your website is an authority in that niche.
- Semantic Relevance & Internal Linking: Well-structured internal linking between related articles tells Google you cover all aspects of a topic and rank better.
- Long-Form, Deep Content Outranks Shallow Posts: Content that answers user intent across multiple subtopics performs better than keyword-stuffed pages.
For example a website about digital marketing that only covers “SEO strategies” may struggle to rank. But a site that builds an SEO content hub with pillar pages, supporting clusters and internal links to related topics (technical SEO, content marketing, link building, on-page optimisation) will establish stronger topical relevance and authority.
Google doesn’t compare a page with another, it compares a topic cluster with others!
Semantic SEO implementation brings better, faster & sustainable rank for any website by enriching topic clusters with reliable info.

What is the role of structured data (Schema) in Semantic SEO?
Google uses structured data (Schema Markup) to understand the context, intent and meaning behind web content. By adding structured data websites can increase their search visibility, get rich snippets and rank better in semantic search.
By adding structured data a business can enhance their search appearance, boost organic CTR and improve discoverability in semantic search.
Here’s how structured data works:
- Enhances Google’s Knowledge Graph Understanding: Schema markup helps search engines associate a website with specific entities, industries and related topics.
- Improves Search Engine Crawling & Indexing: Structured data provides additional metadata about content making it easier for Google to categorise pages correctly.
- Enables Rich Snippets & Enhanced SERP Features: Schema allows websites to appear with FAQ sections, star ratings, product details and more in search results.
For example a food blog that adds Recipe Schema can have its content displayed as rich cards in Google’s recipe carousel, increasing CTR and traffic.
How Semantic SEO Builds Brand Authority & Increases Organic Visibility?
Using semantic SEO, search engines focus on establishing brand authority (trustworthiness) through topic relevance, entity relationships, and contextual depth. Websites that optimise for topical relevance, entity relationship, EEAT, and structured content will gain higher trust signals than keyword-based traditional websites.
In a nutshell, Google matches its own knowledge graph and looks at how have you organised the entities (topics) in depth, compared to Google’s own knowledge graph. If the findings are similar to Google or even better, Google will start giving your website ‘authority’ for that particular niche.
Having a regular higher impression on your webmaster tool indicates that the website is gaining Trust Authority from the search engine. More impression also indicates that web pages will start appearing in search positions better than earlier and the upcoming posts/pages will have a higher chance of ranking.
By investing in semantic search principles, structured data, and authoritative content strategies, businesses can position themselves as industry leaders, ensuring sustained rankings and increased organic traffic over time. Alternatively, a successful semantic SEO implementation will reduce the risk of future downrank for any website.
How does a website pass expertise signal to Google?
Search engine loves brands that demonstrate expertise in a focused niche. Writing valuable and in-depth content indicates that the website knows about its niche better than others. Applying topical maps, topic clustering, and entity optimising will provide better signals about well organising of the topics within the website.
Topic clustering or entity organising through internal links, Schema, and maintaining the information flow tells Google about the website’s exceptional expertise in its niche.
For example, an accountant should not just write about ‘accountancy service’ or ‘tax service’. To gain topical authority, the accountancy website needs to prove its expertise to Google about everything related to the topic and visitors intent it’s serving with the website. Rather than focusing on ‘accounting service’, it needs to cluster focus by adding contents on: accounting ratios, record retention, bookkeeping backlog, bookkeeping error, tax rule changes, special tax circumstances etc.
The topic clustering (distribution of the topical entities) needs to be organised before writing the first content of the website. Because a topical map is not a conceptual map. The topical map needs to cover ever related topics that match with the core topic and core intent.
For example, An SEO agency, offering SEO services in the UK should cover local citation guidelines but explaining what happened at the Saigon SEO conference will not add any value to the visitors.
Google Constantly Communicates with the website and gets trust signals!
If a website is semantically optimised, it can communicate with google in an organised way.

How Does Entity-Based Optimisation Improve Search Trustworthiness?
Google identifies brands as entities in its Knowledge Graph, linking them to relevant topics, people, and industries. A website that consistently publishes high-quality, entity-focused content (adhering to the topical map) is more likely to be categorized as a trusted source.
For example, Google has already recognised Hubspot as a digital marketing expert, Mayo Clinic as a healthcare expert and Backlinko as an SEO expert by mapping entities/topics these websites have been organising, showing expertise to search engines for the past few years.
For our UK business clients, we apply exactly the same practices.
We understand what is your niche, we create a topical map that covers 100% related entities to your niche, we extract the maximum possible user intents/probably questions, and answer the questions by the maximum possible answering angle.
It sounds simple, but this is mathematical, systematic, and takes a lot of time.
How do we create EEAT signal for topical authority in UK?
Google prioritises a website rank based on Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T). We ensure EEAT signals for our UK-based clients in follwing ways:
In summary, we help google to update its’ own knowledge graph by using information from our clients.
How to Build a Semantic Content Strategy & Topical Map?
Building a topical map and semantic content strategy starts with identifying entities (topics) and discovering every possible search perception related to the entities. The final topical map would look like a tree with a silo clustering type. A proper topical map would have a content hierarchy, entity relationships, and contextual optimization.
Unlike traditional keyword-driven SEO, topical mapping / semantic clustering focuses on interlinking topics and semantically related content to establish topical authority and improve search engine rankings.
The best way to build a semantic SEO content strategy using a topical map:
- Identify a broad core topic
- Identify subtopics and related entities
- Extract search intent & LSI for the entities under the broad core topics
- Build topic clusters matching the search intent
- Structure content hierarchy
- Write content keeping the intent first strategy
- Implement internal links based on semantic connections
1. Identify Core Topics & Subtopics (Pillar & Cluster Model)
We start with identifying the main pillar page for any website then connect different topics and ensure there is no risk of cannibalisation. For example, a client offering ‘Tax Advisory Services’ would have a pillar page that purely focuses on tax advising services.
For that pillar page, there would be related entities / semantically aligned topics (subtopics). In this case, related entities could be HMRC, tax reclaim, tax mitigation, tax laws, submission date, filling process, a lot.
The topical map would ensure that each page has a central focus and slightly distributed focus to other connected topics. The pillar page would have 70 subheadings and some of them can have separate pages (if there are enough customers intent to make a separate page).
2. Identify Entities that are not a conceptual topic
There are some entities / relevant topics that are not a conceptual topic. Preparing a knowledge graph through a topic map would require identifying maximum possible of related entities. For that accountancy website, there can be relevant entities that probably are not a conceptual topic. These are:
- Author (as a person)
- Author’s qualification (as a certifying body)
- Areas served
- Timings (working hours, tax submission dates, Tax rates, tax penalty rates etc)
- Partners/team members
- Associated brands, and many more.
Such further entity identification will enrich your entity bank, which is crucial to build a topical map.
3. Extract Search Intents
After you gather the entities, this is time to extract the maximum possible search intents. For example, you need to know what are the stations that might force a person to look for a tax accountant. Knowing the stations or, perceptions would help create the contents in NLP format and satisfy Google BERT & SMART Brain.
We often expand the intent extraction by identifying the variations.
For instance, A person looking for ‘semantic SEO’ might have related intents (perceptions) as below:
- Sudden rank drop
- Competitors outranking
- Educational purpose
- Agency start-up purpose
- SEO degradation through better content
- just curious about topical authority
- Google Penalty
- Webmaster report error
- Less lead conversion, and more.
We then create a set a set Excel pages separating the intents relating to different entities/topics we identified at stage 1.
4. Build topic Clusters matching the search intents & entities in topical map
After having the extracted list of entities, search perceptions, and visitors’ intentions this is time to slowly create the topic cluster. You cannot include all entities and perceptions in a single web page and link them to subpages. It will result in abnormally long content and will no longer be valuable content.
Clustering allows you to separate user intents into different segments. For example, user intents relating to page SEO might have a relation with entities such as Schema, Internal Linking, and NLP but will have the least relation with link-building.
By observing a topic cluster from a top-down approach will help you to understand if there are any significant topic overlays or cannibalization.
- Writing 500 words for the same sub-topic on different pages is a topic overlaying.
- Focusing on the same keywords phrases and user intentions in the same pattern on different pages would create cannibalization.
Overlaying topics in different places would make content less valuable and your website will lose relevance signal.
Cannibalization would confuse Google with which one to trust. You cannot expect two similar pages to have rank for the same keyword phrases.
Get a topical map!
We research and build a topical map for your website. You need to publish content according to the plan and adhere to the semantic content writing rules.

How to Implement a Topical Map & Write Semantic Contents?
A properly optimised topical map will help implement the map within the website effectively. Implementing a topical map starts with writing content in NLP format, linking different sub-topics (related entities) by natural internal linking, and communicating the knowledge graph witha search engine using Schema structured data.
How to write content in NLP format?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) allows Google to understand context, entities, and user intent rather than just keyword occurrences. Writing content in an NLP-friendly format ensures that search engines correctly interpret the meaning of your content, increasing its ranking potential.
We use a maximum amount of N-Grams at a proper sequence so that our contents cover most of the naturally related topics. We also use semantic variations and natural phrases to make the content semantically genuine and enough to satisfy the user’s intents.
We make sure every possible user intents by creating variations of our content parts. For instance, rather than writing about semantic SEO, we talked about what is semantic SEO, how Google knowledge graph works, and how to develop a topical map.
These three example sections cover three different user intents but directly relate to semantic SEO.
We also apply entity-based writing techniques that add sufficient information and correlation for people, places, concepts, and brands rather than just writing about keywords. We make the entities natural by using synonyms and contextual variations. For instance, instead of local SEO, we wrote geotargeted and hyper-local optimisation that enriches the NLP structure.
Get an NLP optimised content for your website.
How to use internal links semantically?
Internal linking helps Google understand your content, content in relation to other topics and assess the depth of your articles. Proper internal linking would help your website give a better topical signal to Google and it will improve crawlability and indexation for the recent and future web pages.
A structured internal linking approach ensures that pillar pages, supporting clusters, and related subtopics are interconnected in a way that boosts search rankings and user experience.
During core updates, Google never compares a page from your website to a page from another web website. Google compares a group of pages (Clusters) to another set of pages from a different website.
This is why topical maps and internal linking are important.
How do we use Schema in semantic SEO to satisfy the knowledge graph?
Uses Schema ensures better communication between your website and the search engine. It results in: Better indexing and ranking, Higher click-through rates (CTR) with rich snippets and Improved visibility in Knowledge Graph results.
We use Schemas such as ‘Organisation’, ‘Article’, ‘News’, ‘Blog’, ‘FAQ’, and ‘Thing Schema’.
In semantic SEO, ‘Thing’ schema is really important it tells Google in a programming language about how many entities have you discussed in your content and how do they relate.
During the time of crawling or core updates, ‘Thing’ schema will be a differentiator for your website.
Here’s an example of ‘thing’ schema’:
Let’s say I have written about semantic SEO that had two major part, which are Topical Map creation and Content Strategy. In the Topical Map there are related entities such as Cluster, Intents, and relevance. There are other concepts that may not be directly related to topical map but relate to Semantic SEO, for example, we talked about Google’s BERT.
The thing schema will tell this exact story to Google in HTML language.
Thing’ schema not only tells google about the entity correlation that you have within your content but, it gives Google links to third-party pages for better understanding.
Here’s how google will see your code: (we have just generated a visualised version of the thing schema we just wrote. This is just an example. We use schema-structured data in different ways to simplify your website’s semantic content network.

This technique costs hours for the SEO experts and they do not offer you quality services. Or, they just ignore it due to lack of expertise.
How to get on the Google’s knowledge graph using semantic SEO?
Publishing semantically optimised content according to the well-designed topical map would make any website enter into Google’s knowledge graph.
Every answer Google makes comes from a knowledge graph Google is currently using. Google does not make its own knowledge bank. The search engine gets reliable, authentic, and useful information from websites and they use this information to answer peoples’ queries.
Assuring search engines with better information than they currently have would help you be in Google’s trusted website list. So, ensuring EEAT, using multiple entities, optimizing entities, using proper internal links, Schema markup, and publishing semantically optimised content will bring your website authority. Having authority represents, Google has started to trust you for the queries relating to your niche.
How to avoid Google algorithm update impacts by semantic SEO?
Best way to avoid Google’s penalty is to obey rules and best practices that relate to copyrighting, content publishing, and link-building. Semantic SEO protects a website by future-proofing it from any Google updates mainly because semantic SEO works for the best interest of Google and do adhere to all of the prevailing guidelines.
Here’s how semantic SEO helps a website rank due to Google penalty:
Semantic SEO reduces search engines’ cost of retrieval. The cost of retrieval represents the time and resources needed for a search engine to crawl a website and understand the activities of a website. Semantic SEO addresses optimising a website through expanding content depth, ensuring EEAT, better internal links, and multi-entity optimisation from different Schema marks up. Alternatively, semantic SEO reduces Google’s time to understand a website.
Semantic SEO helps google reduce its crawling budget and in return, the website gets within Google’s Good Book.
Cost of Semantic SEO
Semantic SEO is expensive. The time it takes to develop a topical map and content optimisation makes the ultimate cost higher. We normally charge GBP 5,000 per month for a large business for applying proper semantic techniques.
However, we have made the semantic SEO easy for small and medium businesses. We have included semantic entity-based optimisation in our Monthly SEO Package which comes under 2000 pounds per month.
Are there any alternatives to Semantic SEO?
Keyword-focused random optimisation is the only alternative to semantic SEO; however, a keyword-focused strategy cannot be a sustainable way to stand out among other competitors. Since, semantic entity-based optimisation is expensive, you can apply the theory partially. But how?
The first stage of semantic SEO is to build a solid topical map. Get it from an expert.
You can get an in-depth website audit report to know the improvement areas and build an effective digital marketing plan.
The next challenge is to write NLP content that partially meets semantic rules. Below are some good practices that will help you write partially optimised semantic content.
How to use CHAT GPT for Semantic SEO?
AI tools like Chatgpt cannot make a topical map or write semantically optimised content for you. However, you can use ChatGPT as an assistant in your entity-based SEO.
These are the ways yo can use Chatgpt in semantic SEO:
