Topical authority is your website’s perceived score assigned by the Search Engine. The term authority represents that your website holds the necessary credibility to Google to write about your specialised topic.
Google doesn’t just rank by keywords anymore. Google ranks a website based on its topical credibility. Google analyses – how deep and how your site covers an entire topic. During the core updates, Google compares a website’s group of pages to another website’s page groups and re-assesses the ‘Topical; Authority’ score.
According to the 2025 quality raters guideline, Google now relates a website’s main purpose to the contents while assessing the authority score. It means just writing on a topic cannot help you achieve the ‘Authority’; however, you need to convince the search engine on ‘ Why you are covering a topic in depth.
Topical authority helps you outrank competitors, even those with higher domain authority or more backlinks. If your website content is appearing on the top search results for the keywords related to a broad topic, it indicates that Google has started to trust your website for that selected topic.
Key benefits of building topical authority:
- Rank for hundreds of long-tail queries and People Also Ask (PAA) results
- Reduce reliance on backlinks by improving internal topical strength
- Increase content trust signals with E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust)
- Dominate semantic search results and improve click-throughs
- Future-proof your website for Google’s Helpful Content and Core updates
This guide breaks down everything from what topical authority is to how Google measures it and, most importantly, how to build authority for your website.
We’ll show you how to:
- Create a semantic content map with topic clusters
- Write for user intent instead of stuffing keywords
- Use AI to find gaps and accelerate smart planning
- Align your content with Google’s Knowledge Graph and NLP ranking systems
- Implement schema, FAQs, internal links, and structured depth that Google rewards
Table of Contents
Who Invented the Topical Authority?
The term topical authority was coined by Koray Tuğberk GÜBÜR, a Turkish Blue-hat SEO expert who has been educating SEO professionals on Semantic SEO under the brand name ‘Holistic SEO Digital’.
However, while Koray gave it a name, Google has long relied on similar concepts under different frameworks. Following the 2013 Hummingbird update, Google shifted its focus from keyword matching to understanding topics and semantic relationships. That was the first start when SEO professionals started implementing LSI keywords instead of focusing on a particular keyword.
The late Bill Slawski, another respected SEO researcher, played a crucial role by breaking down Google’s patents, particularly those related to entity-based search and semantic indexing. His research and interpretations of the patents significantly contributed to other professionals identifying the mechanism of gaining topical authority.
How Topical Authority Increases Website Rank?
Topical authority improves search rankings by helping your website become a trusted source for a specific topic.
When Google sees your site consistently publishing helpful, in-depth, and interlinked content around one topic, it begins ranking your pages higher, even without relying on backlinks.
Google doesn’t search the entire internet for every query. Instead:
- It prioritises trusted websites already in its index & priorised for the topics.
- New content is only fetched if there’s a need for fresh or more relevant information.
- Your Search Console data shows that Googlebot routinely crawls your site to understand your website.
Soon Search engine reveals that your website has published more semantically related content to a broad topic compared to the other websites; it assigns you a place on the list of Trusted Websites.
Usually, single or multiple core updates are needed to appear the search engine’s acceptance.
Here’s an ideal example of a new website gaining topical authority within 30 days:
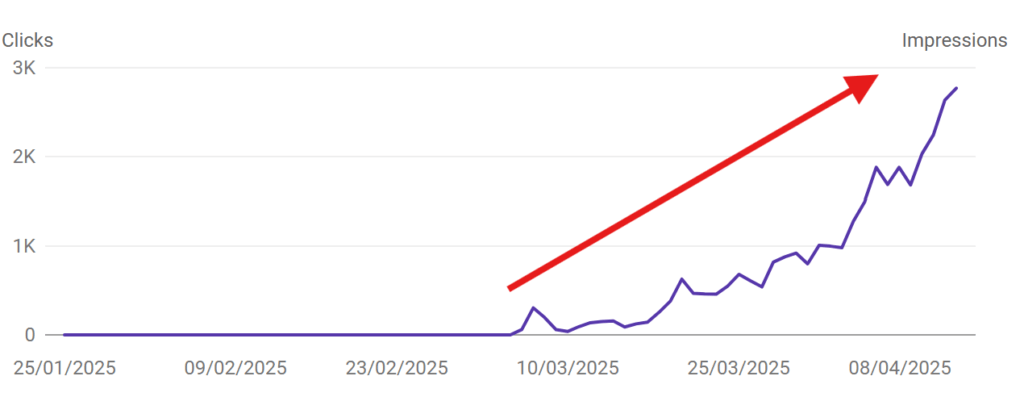
This website touched 3k impressions within 30 days of publishing. With 17 web pages and no backlinks, the website ranks for more than 1500 topically relevant keywords in SERP.
We were lucky that the March 2025 core update rolled out after 8 days of publishing the website.
We followed semantic SEO guidelines to publish the contents, covered topically relevant LSI keywords, and targetted plenty of relevant long-tail keywords.
How Does Topical Authority Work?
Topical authority works by aligning your website content with how Google understands, stores, and retrieves information. It combines search intent satisfaction, semantic/topical relevance, and content depth (proven by the consensus).
Here’s how the topical authority functions through Google’s system:
Google Ranking Methodology: NLP and Topic Clusters
Google now ranks pages by their ability to satisfy broader topic clusters, not the keywords.
Such topical understanding is powered by Natural Language Processing (NLP) models like BERT and MUM, which help Google interpret user intent and contextual relationships between entities.
A well-structured topical map groups related content (pillar + cluster model), linking by the semantic meaning. As a result, Google finds the content easier to understand and interpret.
For example, in this article, I am covering semantically relevant topics to my blog title (core focus of this blog). Also, I am linking other topically relevant pages with meaningful anchor text (not the phrases – ‘click here’).
Cost of Search Retrieval
Google’s algorithm prefers content that’s easier to retrieve and interpret. Google needs to allocate its available resources to the total number of websites.
It’s like spending the same time on two different websites.
Within the retrieval budget, the Google bot will crawl more pages of a website, which is fast, easier to navigate, and designed structurally.
This is how topical coverage and linking the contents based on their meaning affects Google’s cost of retrieval.
This is the reason a web developer should focus on reducing the page size and server response time so that search engines can crawl the website as max as possible.
Google’s Bot needs to understand your content within the preset allocated time
Make your website fast & well structured

Topical Depth vs Brand Signals
While assigning SERP ranking, Google mainly looks at brand signal (popularity of the domain), user engagements, and topical depth. For any new website or small business, the only way to ensure topical depth semantically for achieve search engines’ trust.
Websites with strong topical depth often outperform better-known brands in niche verticals. This happens mainly due to higher topical coverage.
However, a website may still prank contents based on popularity (higher brand search), which requires strong PR anda high marketing budget.
Knowledge Graph and Entity Recognition
Topical authority links closely with Google’s Knowledge Graph, which stores facts about entities (people, places, organisations, concepts) and their relationships. The knowledge graph is how the search engine understands the relationship between the entities.
For example, Google will store the relationships of the entities being discussed in this article. For easy understanding, the search engine will prepare a graph based on what we are discussing here. Such as –
- Topical authority is an advanced SEO technique.
- Topical Authority term was coined by Koray.
Now, Google will retrieve the relationships between the entities such as Topical authority, SEO, and Koray (and use it for future information processing).
E-E-A-T: Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trust
Topical authority is enhanced when content demonstrates strong E-E-A-T signals. Google assesses whether content comes from someone expert and with real-life experience, industry expertise, authoritative credentials, and trustworthy practices.
Pages with unique insights, case studies, or authored by qualified professionals and cited by other sources are rated higher.
However, EEAT can not be made overnight. Adding authors bio or, writing fake experiences cannot boost your website’s EEAT.
Recently, John Mueller (Google’s spokesperson) stated that the EEAT cannot be implemented inside the website. Google has a necessary data validation process to cross-check what you are claiming/writing within the website.
For example, a Search engine can easily assess my credibility from the LinkedIn profile strength and backlinks I have.
Quality Raters Guideline
Google employs human raters who follow the Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines. They assess pages based on E-E-A-T, content depth, and usefulness from different angles as stated by the guideline.
These manual ratings help train Google’s AI systems whether the page is thin, non-value adding, and automated. Google recently updated its guidelines in 2025, where special rules have been set for the AI contents.
This means, if you even ensure topical depth using the AI (without adding the true value of the content), gaining topical authority would be impossible.
How to Gain Topical Authority For a Website?
To gain topical authority, your website must demonstrate thematic depth, relevance, and usefulness across a subject.
To gain topical authority:
- Structure your site around the topic clusters (do not strive for targeted keywords)
- Prioritise semantic depth over single keywords (cover every possible LSI related to the main topic)
- Cover every angle of user intents (Identify and address maximum amounts of queries)
- Add semantic relationships and schema (SO that Google understands the website fast)
- Build trust with helpful content, backlinks, and brand signals
- Target zero search volume keywords for higher featured snippet
- Focus on internal link optimisation
- Avoid canibelisation & bloating the website with identical and irrelevant contents

Here, we outlined the steps of building topical authority:
1. Pick a Topic Instead of Keywords
Rather than chasing keywords, pick a broad topic and cover every possible search entent related to that broad topic.
Selecting a board topic aligns with how Google’s NLP models, like MUM and BERT, process and connect information. These algorithms understand relationships between terms, questions, and entities. Creating content from every possible semantic angle would help these algorithms understand your website nicely, which will help outrank competitors’ websites.
Broad Topic offers you the opportunity to target a group of keywords
Get them all

How would you identify the broad topic?
You need to decide how many steps you are going back to target a broader aspect of a topic. It will again depend on your business model.
For example, this article talks about topical authority, which is connected with semantic SEO, search engine crawling, internal link, schen, and many more.
You need to assess how many vertical & horizontal topical relationships you can make that fall under the core context of the article.
Follow our keyword research checklist for a better understanding.
2. Build a Topical Map with Pillar and Cluster Pages
Topical authority starts with structure. You need to create a topical map that lays out your subject as a hierarchy of pillar pages and cluster content.
A topical map is not a conceptual map. The topical map needs to have contents that cover broad topics supported by the business objective.
For example, SEO is a broad topic, and ‘writing CSS’ is also related to SEO (if you relate to user experience).
However, being an SEO agency in the UK, it doesn’t make sense to publish a blog on how to write CSS. My business purpose is to offer search engine optimisation. In that case, ‘How to minify CSS using lightspeed’ can be a suitable blog topic on the topical map.
Pillar pages are comprehensive overviews of the main topic, while cluster articles dive deep into subtopics and specific user intents.
You can still relate to the content based on the context. It does not matter if the page is from another cluster.
3. Analyse SERPs and Understand Topical Coverage
Before writing, study Google’s Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs) for your topic. Look at the top-ranking pages and identify:
- What types of content rank (guides, FAQs, tools)?
- Which entities and terms do they mention?
- How comprehensive is their coverage? (follow H2,H3 – H5 hierarchy).
If a page only scratches the surface of a subtopic, that’s your opportunity to go deeper. Also, use Google’s “People Also Ask” box to uncover additional subtopics and related intents. Tools like Ahrefs, SEMrush, SEO Minion, Glasp, or Surfer SEO’s SERP analyser can help extract data from top-performing pages.
This approach also helps identify outdated content or pages from weak domains – signs that Google is open to better information.
After you are done with SERP analysis, follow these steps:
- Collect all of the heading (content structure).
- Identify which areas your competitors are covering.
- Add more information to make it helpful (better than competitors).
- Ensure each paragraph immediately answers the query (essential for rich snippet targeting)
- Maintain focus and structural flow of the content.
Find the weaknesses of your competitors’ content, and add up accordingly
Knock them out

4. Make a Semantic Content Plan
After analysing the SERP content, it’s time to structure your content semantically. The purpose of a semantic content plan is to ensure that you have covered every possible angle of the group of queries (LSI keywords).
Here’s how you should create a semantic Content plan:
- Keep the main intent at the beginning of your content.
- Keep the natural flow of the information.
- Create intent variations by adding (What, when, how, who, similarities, dissimilarities, types etc, to cover new angles of the keywords.
- Understand the semantic distance of the topics. Keep the more distant topics for the later part of the article.
- Try to convert subheadings into questions (it increases the chance of appearing in a search snippet).
- Keep the call to action in the later part.
- Do not heavily focus on the nonrelated or semantically distant topics.
5. Identify and Address User Intents
Gaining topical authority would be easy if you could address more user intents than your competitors.
Higher user intent represents better topical coverage and user satisfaction. It also means that search engines would find straightforward answers quickly and reward with featured snipped.
Even the user intents do not have any search volume; write it. It will allow you to gain a featured snippet for questions that your competitors do not cover.
Addressing more intents with organised answers helps a website achieve a sudden gain after any core algorithm update.
We published a separate guideline on how to identify user intents for a topic and optimise them like an expert.
6. Write Content That Addresses Intent and Adds Usefulness
Your content needs to serve the required information that users are looking for. Provide the information straight away. Identifying users’ perceptions and addressing problems straight away also improves the chances of getting indexed for voice search keywords.
For example, if your content title starts with ‘How to, ’ show the steps clearly.
Usually, Google never reads the whole paragraph. Keeping the required information at the beginning of the paragraph would help search engines easily understand the topical coverage of your content.
For further guidelines, read Google’s helpful content guideline and Quality raters guideline to get an idea about value addition and intent matching.
For more, read proven ways of finding blog topic ideas.
7. Avoid publishing Irrelevant content/statements
Why should you avoid publishing too much content?
Publishing so much irrelevant content would confuse search engines about your expertise. However, publishing a massive amount of topically relevant content would also create keyword cannibalisation and drain the website’s rank.
Let me explain how many webpages drain website authority.
Imagine your website having a power of 100. If you have 20 web pages, the power 100 would distribute among the 20 pages through internal links. Publishing 100 contents would distribute the power to every page, and there will be no pages left to support new pages in the future.
Normally, we publish a quality ciintent, wait till the page receives positive impression from search engine and then we create new pages and share the page rank.
In 2025, Google confirmed that publishing a blog irrelevant to the core topic of the website dilutes topical authority (John Mueller, 2025).
This is the main reason for having a structured topical map and following a content cluster. You may go deeper into a topic but slowly after publishing related articles.
You cannot write on On page SEO and jump to – Software selling. You may slowly educate search engines regarding your business intention.
Williams-Cook has revealed a Google API leak where it was evident that Google assigns a ‘Consensus score’ to each paragraph of the content. It means, before assessing the authority, the search engine performs quality checking of the statement and the information we are sharing.
8. Refresh Contents every 6 months
Refreshing content with additional information regularly sends a freshness signal to Google. Google bot regularly crawls our websites. Increase the expectation of Google bot by introducing relevant additional information regularly so that the Bot keeps coming to your website for more information and the search engine assigns you with an increased crawl budget.
A crawl budget is a predetermined timeframe for the Google bot to visit a website.
9. Implement Internal links wisely
Intebral links help users nevigate amin the published contents and Google bot understand a website.
When a crawler visits a website, it follows the internal links to calculate the topical distribution, relevance, and depth.
Use descriptive text in the internal links. Google reads hyperlinks to understand the reason for linking to another webpage. Avoid using ‘Read more’ or ‘Click here. ’
Also, the internal links increase the chance of faster indexing, which affects faster topical authority resulting from quicker indexing and information processing.
Do not use too many internal links as a higher number of internal links drain page rank.
10. Implement Schema Markup for Context
Use structured data (schema markup) to clarify your content’s role. Using Schema, Google understands the type and the purpose of any content.
Schema Markup also helps a website to win the Google knowledge graph faster.
For websites, relevant schema types include:
- Article
- FAQPage
- LocalBusiness
- Service
- Author
- Thing
- Mention
- Product
11. Utilise Brand Signals
While topical depth is crucial, brand mentions and engagement metrics still play a role in Google’s assessment. Google tracks off-site signals to calculate the popularity of any brand.
Your website will achieve a faster rank and authority if people search for the name from different devices and locations.
To get brand signals:
- Mentions of your brand or firm name
- Citations from industry-related blogs
- Links from directories like Yell, Companies House, or Trustpilot
- Frequent brand name search from Google Search
Your SEO strategy should include digital PR, LinkedIn engagement, client reviews, and guest appearances on podcasts or YouTube. These activities amplify your topical trust beyond your website.
12. Expand and Maintain the Topical Map
Topical authority is not a one-time project. As Google evolves and user behaviours change, your content map needs constant refinement. You need to re-read your existing content and look for opportunities to create other content, interlinked content.
It will help add more information and ensure depth of the topic that you are focusing on.
Monitor:
- Existing page (for new content gap)
- News/information to your industry
- Emerging questions on Reddit, Twitter, or Google Trends
- Discover keywords ranking without focusing on the content (use search console)
- Add relevant information, example, and study (contribute to Google’s Consensus score)
Why Do Topical Relevance & Depth Increase SEO Score?
Topical relevance and content depth increase your SEO score by helping Google understand how well your site covers a broad topic. The deeper your content, the stronger its semantic connections across related topics, entities, and intents.
More semantic connections represent a higher amount of long-tail keywords (higher number of intents). It helps a website target more user perceptions related to a broad topic. In addition, Google’s NLP systems, like BERT and MUM, prioritise websites that offer detailed, helpful content with clear topical relationships.
How Does Google Reassess Topical Authority During Core Updates?
During core updates, Google compares a cluster (group of pages) to other clusters from different websites. With the help of historical data, Google re-assesses the depth, relevance, and freshness of the content and assigns a new rank.
The web page cluster of your website would win against the other websites’ if the informations are organised, intent driven and authentic.

How to Measure Topical Authority?
To measure topical authority, the clearest sign is how often your website appears on the first page of Google across a wide range of related queries. If you find that multiple variations of search intent within a specific topic consistently bring your pages to the top results, it means Google recognises your site as a trusted source within that topical area. This is a strong signal of earned topical authority.
Signs of achieving topical authority:
Tools like SurferSEO, MarketMuse, and Clearscope can help assess this by analysing keyword clustering, semantic coverage, entity co-occurrence, and topical depth. These platforms use algorithms to estimate how well your content aligns with other high-ranking sites and how thoroughly you cover related concepts and questions.
However, it’s worth noting that each SEO tool uses its proprietary formula to calculate topical relevance and authority. There’s no official scoring system from Google. Google has never publicly disclosed its method for measuring topical authority—its algorithms evaluate hundreds of signals, many of which remain unknown to the public.
Therefore, the most reliable way to track progress is through performance: more impressions for long-tail queries, more rankings in People Also Ask, and steady improvements in organic traffic across an entire topic cluster.
How to maintain topical authority?
To maintain topical authority, you should:
You need to publish better quality content to exceed Google’s quality threshold. You should also refresh existing content at least twice a year to provide freshness signals to search engines.
A quality threshold is a range that the search engine assigns a website and revises periodically depending on the quality of the content.
Continuous improvements in content quality, better internal linking, and Schema implementation would force search engines to revise the quality threshold to a better position.
Every website performs within the set threshold until a new benchmark (quality range) is assigned. For example, see the image below. In 30 days, the search engine has assigned almost 3 quality benchmarks to the website.
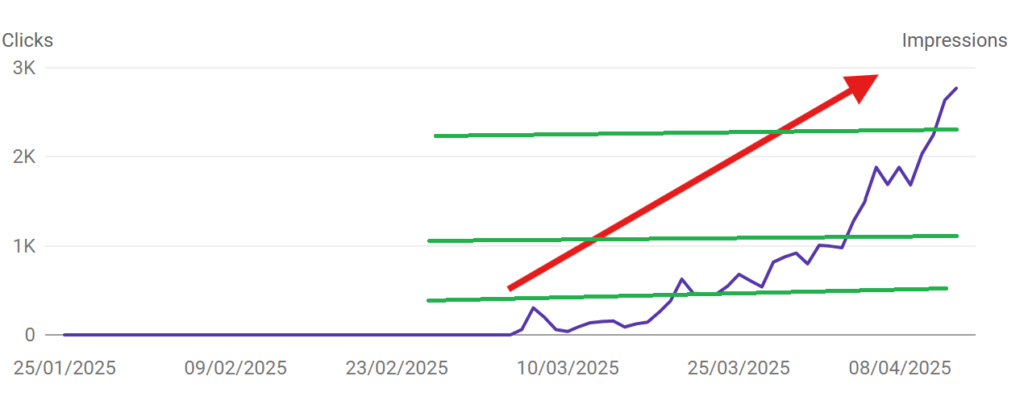
Search engines usually set an upper limit and a lower limit for a website’s ranking performance based on the content quality.
If you are already in the upper range of the search quality threshold, your website’s future content would likely rank faster since Google has already trusted the website.
However, publishing so much content with low value or topically irrelevant could negatively affect the trust and make future ranking potential tougher.
How to get into Google’s knowledge Graph?
To appear in Google’s Knowledge Graph, your website must signal credibility, consistency, and clear entity relationships. Start by using structured data markup (such as JSON-LD) on key pages like your homepage, About page, and author bios. Apply relevant schema types such as Organization, LocalBusiness, or Person to help Google identify what your brand or entity represents.
Next, build citations from authoritative structured databases like Wikidata, Crunchbase, and industry-specific directories. Ensure that your business name, address, website, and description match across all platforms. Inconsistent data confuses search engines and weakens your entity profile.
Semantic consistency is also essential. Use the same terminology and references across your website, blog posts, and external citations to strengthen Google’s understanding of your topical relevance. When Google sees alignment between your structured data, off-page citations, and on-page content, it increases the chances of your entity being connected to its Knowledge Graph, boosting visibility in rich results and brand panels.
How many articles do you need to achieve topical authority?
Topical authority usually appears if you can cover the broad topic within 3 to 4 clusters, maintaining the Silo structure.
However, topical authority cannot be built with more articles as Google focuses on information quality, not the number of articles. You may still become a trusted source to the search engine for a topic with a minimum amount of content, subject to satisfying the search engine that:
Do External backlinks hurt topical authority?
For a new website, external backlinks can drain page rank. We suggest using fewer external links until the website earns enough authority/impressions. However, a website should always use external links to enhance content credibility.
At the initial stage, a new website may only use the reference name instead of linking the websites straight away. Once the authority is achieved, external citations can be done.
Are there any software or plugins for building topical authority?
There are no software, AI tools, or plugins that can truly help you achieve authority for a topic. Plugins are helpful to enhance and speed up productivity only.
To build website authority, you should never rely on any plugins or software since it cannot relate user intent, semantic relations, and the website’s objective within the writings.
Your only job is to provide in-depth, quality content both for the users and search engine and wait till search engine starts trusting the website.
Topical Authority Vs Domain Authority
Topical authority refers to how well a website covers a specific subject in-depth, while website authority (often measured by Domain Authority or Domain Rating) reflects the overall trust, backlink strength, and credibility of the entire domain. A site with high website authority may rank for many topics due to strong backlinks but may not rank well for niche queries if its topical depth is weak.
On the other hand, a smaller website can outperform larger competitors within a narrow niche if it demonstrates topical authority. For example, an accounting blog that covers every aspect of VAT compliance, tax deadlines, and HMRC updates can outrank broader finance websites for those specific queries.
Why is SEMrush’s authority score lower than Moz’s?
Both SEMrush and Moz (and Ahrefs) have their methods to calculate website authority. This is the main reason for having different authority scores in different tools.
Since Google has never disclosed its authority score or its methods, third-party websites try working out the authority anonymously.
SEMrush and Ahrefs do not have access to real & live search console data, which affects a lower number of keyword indexation reports. This can also be a reason for having a varied authority score.
Moz particularly does not account number of featured snippets while calculating domain authority. As soon as you have backlinks, Moz’s authority score keeps increasing, which should not be considered as a decision-making tool.
How to use AI in building topical authority?
AI can help increase your topical authority by speeding up the process, research, and brainstorming.
For example, you can use ChatGPT for brainstorming a broad topic, which results in the discovery of new keyword intents.
Humanising tools like Surfer can help you add missing entities by analysing the overall context of the article.
The deep research function of the large language models can help you incorporate consensus into your writing for better credibility.
We do not recommend automating a topical map, blog generator through AI, as Google strictly prohibits that.

