You should not blindly rely on AI content. AI-based large language models such as ChatGPT, Gemini, and Perplexity can be used to help with content writing. Still, human effort is essential for tonality, fact-checking, sentence restructuring, and personal experience input to make the article trustworthy and valuable for users and search engines.
Thanks to advancements in AI tools, AI-generated content has become a staple in digital marketing. Yet, despite its popularity, AI-written articles often struggle to rank well in Google’s search results. That’s because search engines prioritize high-quality, user-focused content that shows experience, expertise, authority, and trust (EEAT). In its current form, AI can’t produce content that fully meets these standards.
Google’s recent algorithm updates have made it clear: originality, usefulness and depth are key to ranking content. AI-generated text relies on predictive models and pre-existing datasets, lacks contextual understanding, real-time updates, and human-like engagement. It’s just not the same as content created by a human. (Google recently updated their spam policy in 2025, indicating that any actions to that trick search engine algorithm will be considered spam. Content automation directly falls under this policy as with a bundle of articles, a website may influence search engines for better authority and acceptance.
So, should businesses rely solely on AI-generated content for ranking? The answer is no. AI can be a helpful tool for content creation, but human oversight is necessary for originality, credibility and SEO.
Key Takeaways of why solely depending on AI-based content can be harmful:
✔ AI content doesn’t rank because it’s not original, not deep and not real world expertise. Google favors content with strong E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness).
✔ Google doesn’t penalize all AI content, but devalues low quality mass produced AI text that’s not been humanised and adds no value.
✔ AI models use old data, so AI generated content contains outdated or incorrect information. Industries like finance, law and healthcare need constant updates that AI can’t provide.
✔ AI content lacks topical coverage as it doesn’t go into semantically related subtopics, resulting in thin content that doesn’t rank well.
✔ AI generated text sounds robotic, hurts readability and user engagement. Google’s NLP algorithms detect unnatural patterns and ranks accordingly.
✔ First hand experience and expertise is key to rankings. AI can’t provide real world case studies, professional insights or verified data which makes it less credible.
✔ Google’s algorithms detect AI written content through linguistic patterns, engagement metrics and topic relevance. Low quality AI content can trigger algorithmic suppression.
✔ To humanise AI content, businesses need to rewrite robotic text, add expert insights, improve topical coverage and optimise readability.
✔ Websites affected by algorithmic penalties need multiple core updates to recover. Google stores website data for 13 months, so changes take time to reflect in rankings.
✔ AI assisted content can rank if it’s been edited, fact checked, enriched with first hand expertise and structured for SEO.
Table of Contents
Understanding AI-Generated Content
What is AI-Generated Content?
AI-generated content refers to any type of content, be it text, images, or videos, which are created using artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms such as ChatGPT or Gemini. These large language model (LLM) algorithms leverage machine learning and natural language processing to produce content that often mirrors human creation.
From marketing materials to entertainment, AI-generated content is becoming increasingly used across various web-based industries (mainly in website SEO).
How does AI create an article?
Initially, the AI system is trained on a large dataset of existing content, such as text documents or image libraries.
This training enables the Large Language Model (LLM) to understand patterns, styles, and structures within the data.
Once trained, the Artificial Intelligence-based tool, such as ChatGPT, can generate new content by applying these learned patterns and given sets of data.
The process can be fine-tuned to produce content that adheres to specific styles, tones, or formats, making it highly adaptable to various needs. This capability of AI-generated content to mimic human writing or artistic styles is powered by advanced algorithms and vast amounts of data.
Benefits of AI-Generated Content
The use of AI-generated content offers several compelling benefits, such as increased efficiency, improved consistency, enhanced creativity, and cost savings.
- Increased Efficiency: AI-generated content can be produced much faster than human-generated content, making it ideal for time-sensitive applications.
- Improved Consistency: AI systems can create content to a consistent standard, minimizing the risk of errors or inconsistencies.
- Enhanced Creativity: AI algorithms can generate unique and innovative content, which is particularly valuable in creative fields.
- Cost Savings: Producing content with AI can be more cost-effective than relying solely on human writers, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious businesses.
Why AI-Generated Automated Articles Fail to Rank?

AI-generated content fails to rank because it often doesn’t meet Google’s ranking criteria for useful, reliable and engaging content. Most importantly, tools like ChatGPT uses backdated or irrelevant data.
Do AI-Generated Articles Violate Google’s Guidelines?
AI-assisted writing isn’t against Google’s policies, but using an AI text tool to generate content with the intent to manipulate rankings is considered spam per Google’s spam update guidelines 2025.
Secondly, content automation refers to scaled content that violates Google’s core update guidelines as stated by the Core Algorithm update in March 2025 and 2024.
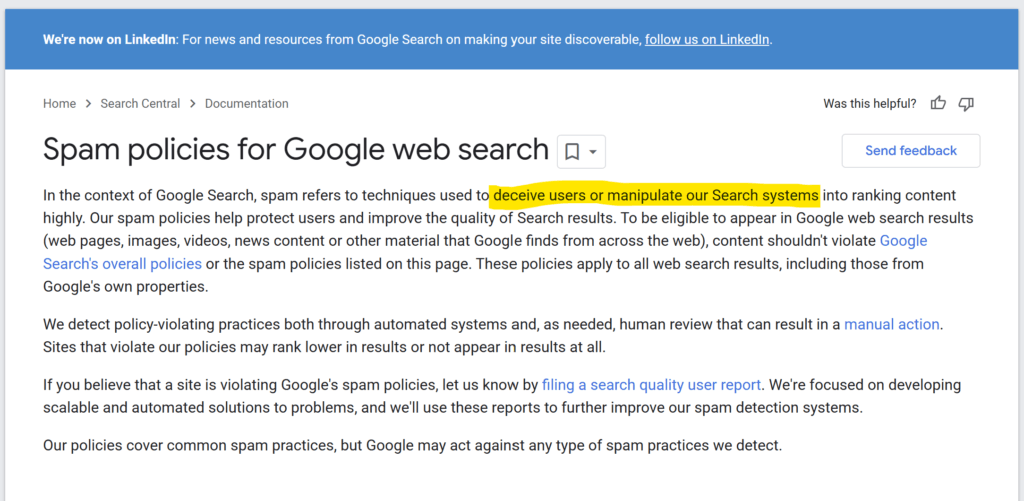
“Using automation including AI to generate content with the primary purpose of manipulating ranking in search results is a violation of our spam policies.” – Google Search Central
Google’s algorithms evaluate content based on whether it genuinely serves users or is created for SEO gains. Generating content to trick search engine algorithms also violates guidelines stated by Google’s Helpful Content Guidelines.
Here’s a screenshot of Googlke’s Spam Policy (revised on 2025)
Why Does AI Produce Old or Inaccurate Data?
AI-based writing tools use old or inaccurate data mainly because of outdated training data, inability to capture the writing prompts, inability to understand the context,t and due to technical limitations.
- Outdated Training Data: If the dataset used to train the AI is outdated, the generated content may reflect obsolete information. For example, ChatGPT uses data available on the internet.
- Biased Data: Training data that contains biases can lead to biased content generation, affecting the accuracy and fairness of the output. For example, AI always tries to validate your writing instructions without checking the authenticity.
- Lack of Context: AI algorithms may not fully grasp the context in which the content is used, leading to potential inaccuracies or inconsistencies.
- Technical Limitations: AI systems are not infallible and can make mistakes, resulting in the generation of incorrect data.
AI-generated articles struggle with timeliness and accuracy because AI models rely on pre-existing datasets rather than live information retrieval. AI systems don’t have access to real-time industry reports, regulatory changes or dynamic market trends.
For example, AI-generated content about VAT thresholds may show outdated figures. Today, I asked CHATgpt to write an article on VAT for one of my accounting firm client. AI referred to VAT threshold of 85000 instead of using latest information – 90000.
Why Does AI Content Lack Topical Coverage & Semantic Depth?
Google rewards in-depth, authoritative content that answers user’s query comprehensively, but an AI-powered tool often fails to apply topical coverage because it mainly operates on single-prompt keyword inputs rather than expanding topics holistically.
Easily – ChatGPT writes an article based on our instructions but, without observing already published articles in our websites.
For instance, if an AI tool is asked to write an article on “Company Accounts,” it may only cover the basic definition rather than covering:
✔ Company accounts filing deadlines
✔ HMRC penalties for late submissions
✔ Micro-entity vs. full statutory accounts
✔ How accountants structure company accounts
This lack of semantic depth and contextual expansion results in thin content that ranks poorly. Again, preparing a THIN content is a direct breach of Google’s Helpful Content Guidelines.
Human-written content naturally connects related subtopics, strengthening topical authority which is key for Google rankings.
Moreover. A large language model can’t think like an expert.
Let’s say, I have been in the SEO industry for about 15 years and I know that writing an article on AI-based tool would include information from already published websites, not from the experiences of the author.
This is the main reason why affiliate websites are losing their rank. Most of the affiliate website owners are not experienced in that field, taking the help of a language model to generate content and subsequently falling under Google’s quality threshold mainly due to less topical coverage and experience signal.
Why AI-Generated Articles Destroy Writing Tone & Readability?
Articial content writing tools use preset information and a single set of instructions while writing an article. AI contents do not reflect the author’s personal experience, real-life examples, and NLP writing patterns. That’s why Google either doesn’t understand the website or devalues the website’s trustworthiness.
Main reasons why AI destroyed article tone and readability:
✔ Overuse of generic phrases and unnatural sentence structures.
✔ Lack of personality, conversational flow and brand alignment.
✔ Repetitive sentence patterns that negatively impact user engagement.
Google’s engagement metrics such as bounce rate, dwell time and user interactions play a huge role in content ranking. When AI-generated text feels robotic, users leave the page quickly, telling Google that the content is low quality. Similarly, when automated writing patterns do not address the intent of the readers, readers leave the website, which ultimately decreases the website’s SEO score.
Here, we wrote about 12+ proven AI strategies to effectively design website content.
Why AI Articles Lack First-Hand Experience & EEAT Signals?
AI writing tools cannot bring real life experience because the first-hand experience comes from the brain, related to the context. And without the first hand experience and authentic data, an article is unlikely to pass Google’s EEAT (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) framework
Let me tell you why!
At the time when I am writing this article, I know which example to use in what context. I have tried generating AI-based content for the last 15 years. So, my examples matched with the context of this article. If I instructed ChatGPT to use an example, it would have used fake examples or copied from other authors.
A human-written SEO case study may include real business challenges, applied strategies and measurable improvements. For example, I gave a VAT threshold reference of GBP 90k (which was 85k earlier), and ChatGPT used that old figure.
The real experience or the story can be validated by other sources such as Linkedin, GMB or the author’s social profile. Let’s say I am claiming a 15 years of experience, Google will surely validate this information from my social network or from alternative sources.
Similarly, AI-generated content fabricates generic case studies without real-world validation, reducing credibility. If you as k AI to use an example, it starts pulling off fake experiences that cannot be supported by other information source.
Why AI-Generated Content Fails to Maintain Contextual Focus?
AI-generated content can lose contextual relevance because it lacks deep understanding of audience intent and business objectives. To win topical authority in any niche, a website’s content needs to align between the business objective and the users’ intent.
For example:
- A professional accounting firm writing about tax compliance may need industry-specific case studies.
- AI-generated text may generalise the topic without considering jurisdictional differences or legal compliance factors.
Ask AI about preparing article VAT rules. The article will surely cover information about VAT penalties but will not be able to justify any prior experience of saving a client from an HMRC penalty just because it doesn’t have that level of expertise.
We’ve tested CHATGPT to produce accounting articles. It does generate informative articles but, the contextual relationship is missing. For example, an accountant will relate VAT rate with business type and situation.
Let’s say, if the accountant is writing about VAT returns for pharmacies, he will focus on pharmacies receive a PPD statement (income statement) from NHS in two months’ arrears and VAT needs to be submitted each month. The accountant will relate the cash flow in this context that AI AI-based language model will fail to identify these contextual gaps, only because of not being an expert.
Since Google’s Search Quality Guidelines emphasize content relevance, AI-generated articles that fail to align with specific audience needs tend to rank poorly. Tools that can humanize ai text absolutely are essential to bridge this gap.
Why Highly Automated AI Content Falls Under Google’s Spam Algorithm?
Google has rolled out multiple algorithm updates targeting thin, mass-produced AI content. Websites that scale AI-generated articles without human oversight often face content suppression and ranking penalties.
The March 2024 Google Core Update targeted low-quality AI-generated pages with high keyword stuffing and low readability, resulting in significant ranking drops for affected websites. In March 2025, Google announced another core update to reward quality content that is made to satisfy users.
Google is heavily focusing to priorise small business or creative publishers. rewarding software will devalue Google’s priority to both users nad the publishers.
What Is Thin Content? How to Add Value to AI-Based Content?

Thin content is content that doesn’t provide substantial value, depth, or engagement to users. An appropriate example of thin content would be to discuss a product, not analysing a product’s performance, and make necessary comparisons and recommendations from real life experience and the author’s judgment.
An ai humanizer tool can help transform AI-generated articles into more valuable, human-like text by adding detail and semantic richness. However, manual efforts such as data correction, first hand experience inserting and sentence restructuring would be needed to make the content useful.
Follow these guidelines if you want to make your content valuable:
✔ Expand content with first-hand insights, industry data and case studies.
✔ Ensure NLP-based keyword integration and strong semantic SEO by adding related topics
✔ Improve readability, formatting and internal linking.
Does Google Detect All AI Content?
No, Google doesn’t detect all AI-generated content nor penalises AI-assisted writing by default. Google only penalises fully automated content that lacks value, originality and human touch.
Algorithms including RankBrain, Neural Matching and the Helpful Content System are designed to assess content quality not just AI involvement. In fact, Google does not have any direct problem with AI tools to improve readability. The only concern of the search engine is not mass production of automated articles without addressing users’ value.
Google’s spam policies target mass-produced, low-quality AI content created to manipulate rankings. However, AI-generated content that is edited, fact-checked and enriched with expert insights can still perform well in search rankings. The key factor is whether the content meets E-E-A-T criteria and provides value to users.
Since Google focuses on user engagement metrics, semantic depth and credibility, AI-assisted content that includes human intervention, unique perspectives and structured information remains rankable. Websites that rely purely on automated, generic AI content without value addition risk algorithmic demotions or manual penalties.
How to Humanise AI-Generated Content with Human Intervention?
AI-generated content lacks originality, depth and credibility. To make it rank-worthy, manual refinement is required to remove AI footprints, add value and improve readability.
Here are our Humanising guidelines for AI-written content.
1. Remove AI Footprints & Improve Readability
AI-generated text follows predictable patterns, making it robotic and repetitive. Try to manually edit the sentence, bring your tone.
- Vary sentence length and structure to improve readability.
- Change the sentence structure like you talk to someone
- Avoid overused transitions like “In this article, we will discuss.”
- Remove words like delve, in the testament etc.
2. Add First-Hand Experience & Real Insights
Google prioritises content that demonstrates real expertise and unique perspectives. While AI tools can assist in content creation, adding first-hand experience and real insights is crucial.
- Include case studies, real-world examples or professional insights.
- Use industry-specific terminology and provide actionable guidance.
- Cite reliable data and practical strategies. Example: AI: *”Backlinks improve SEO.”\
- Humanised: “A strategic backlink campaign increased our client’s organic traffic by 32% within six months.”
3. Add Semantic Depth & Topical Coverage
AI-generated content lacks comprehensive coverage of a topic. Expanding on key areas improves search engine optimization and search performance.
- Cover related subtopics and long-tail queries.
- Integrate Google NLP-based entities for better keyword relevance.
- Use internal linking to boost topical authority.
Example: If AI writes about corporation tax, expand with:
- HMRC tax filing deadlines and penalties.
- Tax-saving strategies for different business structures.
4. Strengthen EEAT (Experience, Expertise, authority, Trust)
Google ranks content that shows subject expertise and credibility. Bring trust factors such as references to your LinkedIn post or YouTube videos. Relate any university study or link with any of the case studies that you have published earlier.
- Add expert insights, case studies and professional commentary.
- Use citations from government sources and industry research.
- Fact-check and provide practical advice.
- Include research data
- Link to case studies
- Mention your social media posts (that talks about unique findings)
Example:
AI: “Tax planning is useful for businesses.”
- Humanised: “Businesses that do quarterly tax reviews can reduce their liabilities by 15% annually.”
5. Optimise Formatting for Better Engagement
- Use bullet points, numbered lists and clear subheadings.
- Include visuals, tables and structured data where relevant.
- Ensure call-to-action (CTA) placement aligns with user intent.
How to Add Topical Coverage in AI-Based Content?
AI-generated content lacks depth and doesn’t cover all semantically relevant aspects of a topic. To improve topical coverage and boost SEO, manual refinement is required. Include semantically relevant topics. Follow our guide on the keyword research checklist to cater more related topics in the article.
Expand with Related Subtopics
AI-generated text focuses on primary keywords but misses contextual depth. Identify and add supporting subtopics to complete the content. For example, brainstorm, analyse competitors’ websites, and do some research to find out missing topics that are somehow related to the core context of the article.
- Use tools like Google’s “People Also Ask” and related searches.
- Include variations of the main topic, such as industry applications and case studies.
- Bring up topics that have been discussed by the competitors and add more information on those topics
- Find missing topics that your competitors have not covered and write about those by making contextual connections within the writing.
Use NLP & Semantic SEO
Google’s Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithm looks for keyword relationships within content. AI can’t naturally integrate these, just as it may struggle to define a specific art style in generated images.
- Add Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords to improve context.
- Structure content with Google Knowledge Graph entities.
Analyse Competitor Content for Gaps
AI-generated content misses key elements found in high-ranking competitor pages. Using an ai image generator can help create unique visuals that complement the text.
- Review top-ranking articles and note missing subtopics.
- Add expert insights and updated industry data to complete.* Connect AI-generated content to existing content on related topics.
- Use anchor text to strengthen topical relevance.
How to Get a Website Out of an Algorithmic Penalty?
Getting out of a Google algorithmic penalty requires content optimisation, site authority and compliance with ranking guidelines. Google stores website data for 13 months so changes made today may impact rankings in the next core update but full recovery can take multiple updates.
1. Find Out Why You Were Hit
- Check Google Search Console for ranking drops, indexing issues or manual actions.
- Compare traffic before and after the algorithm update.
- Identify thin content, AI-generated spam, poor quality backlinks or bad user experience as the possible cause.
2. Remove Low-Value Content & Improve Quality
- Delete or rewrite thin, duplicate or AI-generated pages with little engagement.
- Add first-hand experience, expert opinions and credible sources.
- Improve E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trust) by adding author bio, case studies and credible references.
3. Fix Technical SEO & User Experience Issues
- Fix page speed, Core Web Vitals, mobile usability and structured data errors.
- Internal linking to enhance topical authority.
- Ensure correct indexing in robots.txt and XML sitemaps.
4. Remove Spammy Backlinks & Build Authoritative Links
- Use Google’s Disavow Tool to remove toxic or irrelevant backlinks.
- Earn links from industry-relevant sources through digital PR, guest posting and expert contributions.
5. Monitor & Adjust
- Track progress over multiple core updates – changes take time to show.
- Continue content updates, backlink monitoring and UX improvements.
- Expect partial recovery within one update but significant gains over multiple core updates.
SEO Opportunity – How Can UK Accountants Win the “Childcare Accountant” Niche?
You can win the “childcare accountant” niche with SEO because UK search demand is high, competition quality is low-to-medium, and…
Different Niches for Accountants in the UK: a data-led SEO playbook
Specialising in a tightly defined niche helps UK accountants win more qualified leads, rank for specific intent keywords, and close…
SEO for Financial Advisors: The Complete Guide to Ranking, Leads, and Trust
SEO matters for financial professionals because it tackles three challenges at once: visibility, credibility, and conversion.First, you need to…
To rank higher in AI-driven search engines and voice search results, you must optimise your website for voice search by…
Topical authority is your website’s perceived score assigned by the Search Engine. The term authority represents that your website holds…
How to use AI & ChatGPT for Article writing & blogging? 16 Effective Strategies
AI tools like ChatGPT are a must-have for bloggers and content creators. 63% of marketers now use AI for content…






